#C241118A. 树
标签(Label)
- 树的直径
网址(Website)
题目(Problem)

样例
输入数据 1
6
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
3 6输出数据 1
1 1 2 4 6 6【样例 1 解释】
$k = 4$ 时,联通块为 ${1}, {2}, {3}, {4,5,6}$。
输入数据 2
5
1 2
2 3
3 4
3 5输出数据 2
1 1 3 5 5【样例 2 解释】
$k = 3$ 时,联通块为 ${1,4,5}, {2}, {3}$。
【样例 3】
见选手目录下的 $tree3.in$ 和 $tree3.ans$。
该样例满足子任务 $2$ 的限制。
【样例 4】
见选手目录下的 $tree4.in$ 和 $tree4.ans$。
该样例满足子任务 $5$ 的限制。
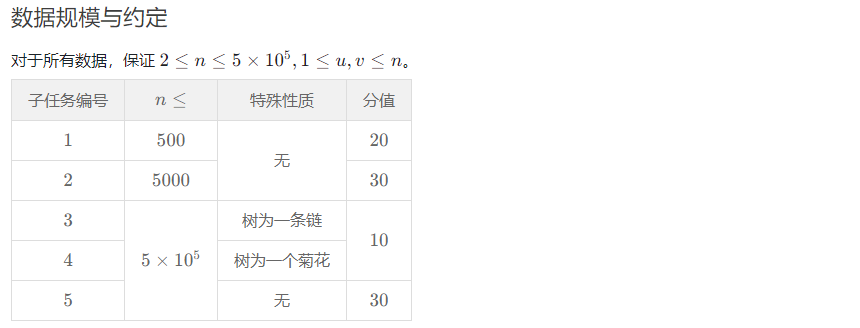
题解(Solution)
性质一:在树的直径上,令直径两端为 $x,y$ ,那么距离直径上的点 $i$ 距离最远的点一定是 $x$ 或 $y$ 的其中一个。
性质二:在以上的条件下,距离不在直径上的点 $j$ 最远的点一定是 $x$ 或 $y$ 的其中一个。
那么直接求出所有的点最远的距离,然后以距离为下标存入数组中,从 $n$ 到 $1$ 枚举最长距离,然后计算连通块即可。
时间复杂度:$O(n)$ 。
出题者题解

代码(Code)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#define For(i,l,r) for(int i=l;i<=r;i++)
#define Rof(i,l,r) for(int i=l;i>=r;i--)
using namespace std;
#define P pair<int,int>
#define int long long
#define x first
#define y second
inline int rd(){
char c;bool f=false;while(!isdigit(c=getchar()))f=c=='-';int x=c^48;
while(isdigit(c=getchar())){x=(((x<<2)+x)<<1)+(c^48);}return f?-x:x;
}
inline void write(int x){
if(x<0) putchar('-'), write(-x);
else if(x<10) putchar(x+'0');
else write(x/10), putchar(x%10+'0');
}
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 501234;
bool ST;
double Tim;
vector<int> ft[N];
int n,root1,root2,len;
int dis[N];
void dfs_dis(int x,int fa){
dis[x] = dis[fa] + 1;
for(auto y:ft[x]) if(y^fa) dfs_dis(y,x);
}
bitset<N> vst;
void dfs_vis(int x,int fa,int to,int step){
if(x==to) return vst[x] = true, dis[x] = max(len-step, step), void();
for(auto y:ft[x]) if(y^fa){
dfs_vis(y,x,to,step+1);
if(vst[y]) return vst[x] = true, dis[x] = max(step, len-step), void();
}
}
void dfs_tag(int x,int fa){
for(auto y:ft[x]) if(!vst[y]) vst[y]=true, dis[y] = dis[x]+1, dfs_tag(y,x);
}
int v[N],as[N];
int fa[N];inline int find(int x){
if(x==fa[x]) return x;
return fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void Solve(){
n=rd();For(i,1,n-1){
int x=rd(),y=rd();
ft[x].emplace_back(y);
ft[y].emplace_back(x);
}
dis[0] = -1, dfs_dis(1,0);
For(i,1,n) root1 = dis[root1]>dis[i] ? root1 : i;
dis[0] = -1, dfs_dis(root1,0);
For(i,1,n) root2 = dis[root2]>dis[i] ? root2 : i;
len = dis[root2];//树的直径
dfs_vis(root1,0,root2,0);
For(i,1,n) if(vst[i]) dfs_tag(i,0);
For(i,1,n) v[dis[i]]++;
int leijia = 0;
Rof(i,n,1){
leijia += v[i];
as[i] = min(n-leijia+1, n);
}For(i,1,n) write(as[i]), putchar(' ');
}
bool ED;
signed main(){
cerr<<abs(&ST-&ED)/1024./1024.<<"MB\n";
freopen("tree.in","r",stdin);
freopen("tree.out","w",stdout);
int Tt=1;Tim=clock();
while(Tt--) Solve();
return cerr<<"TIME:"<<(clock()-Tim)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC,0;
}


